We’ve obsessed with Artificial Intelligence and its ramifications enough – from the automation threat to its wide ranging applications in saving our species. Modern healthcare too, is poised for an impact on multiple such parameters.
Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare Diagnosis
The medical industry is facing a shortage of doctors, nurses, and other healthcare assistants to respond to the growing needs of medical care of the population. A sufficiently artificially intelligent technology will allow robots & computers to self-work without human directions; improving the quality and availability of healthcare services. Basic AI assistants can provide online care & threshold level help to patients, without the need for hospital visits. Thus, an AI assistant may cover up a large part of clinical services and free up doctors’ time to attend more critical cases. AI algorithms can quickly analyse millions of samples in short order and discover useful patterns. Thus changing the way medical science works.
Neural Networks and Deep Learning in Modern Healthcare-
Also Read: The Internet Of Things Is the New Future Of The Healthcare Industry
Neural networks are a computational concept based on a large collection of neural units, loosely modelling just the way our brain analyses. Our brain solves problems with large clusters of biological neurons connected by axons. Each neural unit is connected with many other units which are self-trained rather than explicitly programmed. In the case of AI, the neural network has the ability to learn from its previous cases. Artificial neural networks can diagnose diseases fast & accurately like eye problems, malignant melanoma etc.
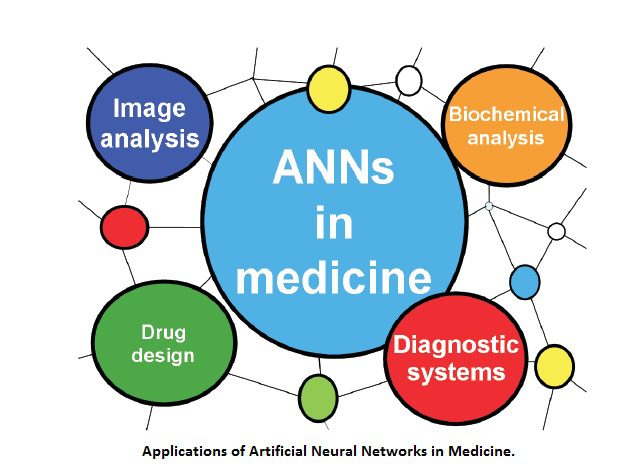
ANNs (Artificial Neural Netowrks) are a powerful tool to help physicians perform diagnosis and other operations. They helps in processing the large amount of data in less time, reduction of diagnosis time, etc. ANNs have proven suitable to detect heart and cancer problems, to analyse blood samples, to track glucose level in diabetics, tumour detection using image analysis, development of drugs, etc. It is making the analysis more credible and increasing the patient satisfaction.
In medical diagnosis, deep learning is expected to extend its roots into medical imaging, sensor-driven analysis, translational bioinformatics, public health policy development, and beyond. The deep learning technique emerged as a result of artificial neural networks. It serves as a powerful tool for machine learning, reshaping the future of artificial intelligence. Deep learning systems are used where human interpretation is difficult. This can make diagnoses of diseases faster and accurate thus reducing the risk in the decision-making process. Deep learning mainly depends on large amounts of training data. Such requirements make more critical the classical entry barriers of machine learning, i.e., data availability and privacy. It could save lives, and avoid medical complications.
Deep learning has gained a central position in recent years in machine learning and pattern recognition. Deep learning shouldn’t be considered a tool for every single health challenge; it is still questionable whether a large amount of training data and computational resources needed to run deep learning at full performance is worthwhile. Deep learning has provided a positive revival of Neural Networks. Deep learning may slow down the development of machine learning algorithms with conscious use of computational devices.
Let human do what they do well and let machines do what they do well. In the end, we may maximise the potential of both.
Available AI Interfaces
Google DeepMind
DeepMind was founded in 2010 by Demis Hassabis, Shane Legg and Mustafa Suleyman. The team combined machine learning and system neuroscience to build learning algorithms. Google acquired the startup in 2014. DeepMind algorithms have shown considerable potential. They remember previously solved problems and use the data to solve new ones if required.
- In July 2016, DeepMind collaborated with Moorfields Eye Hospital to apply DeepMind technology in the analysis of eye scans, searching for early signs of diseases leading to blindness.
- A month later, with the researchers of University College London Hospital, DeepMind announced an algorithm that can accurately differentiate between healthy and cancerous tissues in head and neck areas.
- Also in 2016, DeepMind collaborated with Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust to assist in the management of acute kidney injury.
IBM’s Watson
IBM’s Watson was launched in 2010. Watson is a supercomputer which blends artificial intelligence and analytical software for optimal construction of questioning and answering. Its aim is to interact the way humans do, across a range of applications. And it processes, understanding the questions that humans ask and providing answers that humans can understand and justify. It has helped to change the way medical field works.
- With the help of deep learning and the medical images, Watson is used to diagnosing melanoma, a form of skin cancer. The software recognises features of the disease and may guide the treatment process.
- Recently IBM’s Watson is was used in diagnosing and treating cancer of some 200,000 patients in Manipal Hospital, India when patients outnumbered the doctors.
- A Neutrino App Powered by Watson was launched to help pregnant women track her health. It acts as a nurse guiding one with the dietary needs, health goals, food preferences, eating habits, etc. to a woman’s needs throughout her pregnancy.”