You may get high-quality care with far less downtime thanks to robotic surgery. Healthcare is delivered precisely, even to inaccessible regions, thanks to cutting-edge technology. Robotic surgery systems treat various medical issues involving the heart, digestive tract, bladder, and prostate.
This article will briefly examine robotics in surgery, its history, and its current and future applications. Without further ado, let’s jump into the explanation!
What is Robotics in Surgery?
In robotic surgery systems, sophisticated equipment extends your surgeon’s skill set. This method allows surgeons to access previously inaccessible areas and complete complex procedures through minimally invasive means. Precise motion and improved magnification are two further advantages of robotic surgery.
Robotics in surgery includes:
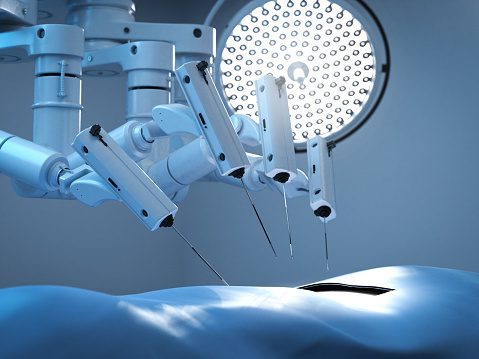
- Microsurgical tools mounted on surgical arms with wrist attachments.
- A unique camera that captures the surgery site’s high-resolution, stereoscopic 3D images.
- Console at which a surgeon directs the movements of surgical instruments and cameras.
The surgeon will sit at a console. This is where they have a precise view of the action and can direct the instrument’s flow as he sees fit. At the control panel, they may see live, 3D visuals in high resolution. While the patient is being operated on, their cart is maintained adjacent to the bed. The camera and surgical tools are stored on the patient cart. The third part, the vision cart, facilitates effective communication between all the parts. Depending on the system, various parts may be used for surgical procedures.
Types of Robotic Surgery

The types of robotic surgery are as follows:
- Robotic Gynecologic Surgery: Some women may choose robotic gynecologic surgery over open or laparoscopic treatments. Open gynecologic surgery, which requires a big incision in the belly, has been the norm for years.
- Robotic Prostate Surgery: According to studies, radical prostatectomy is one of the most successful treatments for prostate cancer. US surgeons utilize open, laparoscopic, or robotic-assisted laparoscopic surgery already.
- Robotic Colorectal Surgery: Surgeons remove malignant and benign tumors and polyps during a robotic colectomy. A robot-assisted method helps surgeons reconnect the colon after eliminating cancer. The treatment may be done with many little incisions instead of one big one.
- Single-Site Robotic Gallbladder Surgery: Medications and lifestyle modifications are used to treat gallbladder disease. In certain circumstances, physicians advocate gallbladder removal (cholecystectomy).
Applications of Robotics in Surgery
Due to the lack of conclusive scientific data showing more significant rates of surgical problems with robotic surgery systems compared to traditional or even laparoscopic surgery, it is considered promising in many medical disciplines. Plus, research shows the advantages of robotic surgery over other modes of surgical access, such as improved surgical ergonomics and a more accurate three-dimensional view of the operating field compared to conventional laparoscopy.
However, the size of materials, the limited flexibility of power devices, and the difficulty of performing procedures that employ multiple quadrants or surgical sites are presented as negatives. Surgeons still need more ready access to the necessary technology and education.
Talking of robotics in surgery history and its current and future applications, In 1993, Alberto Roveda conducted a liver biopsy through robotic surgery systems on a pig; the surgical station was in the Laboratory of NASA in Pasadena, California, while the pig was in Milan. As a result of these and other observations, commercial activities involving robotic surgery have begun, with the first robot utilized being AESOP. This mechanical arm controlled the optical movement on video surgery with voice command. By 1997, Jacques Himpens and Cardiere had conducted the first of the many types of robotic surgery in Brussels using the Zeus and Da Vinci surgical systems. Since that time, this technique has been used for a wide range of treatments.
Limitations of Robotic Surgery
The limitations or risks of robotic surgery include the following:
- Restricted to hospitals with sufficient funds and highly skilled surgeons.
- In the event of difficulties, your surgeon may need to switch to an open operation, requiring deeper incisions. Previous surgical scar tissue is one such factor that might hinder the use of robotic technology.
- Compression and injury to nerves may occur.
- Rare robotic failure to perform correctly.
Conditions Where Robotics in Surgery is Used
Robotics in surgery has been effective for a wide variety of ailments. Following are procedures that have been successfully carried out with robotic surgery systems.
- Treatment involving the heart
- Treatment involving the urinary tract (urology).
- Endometriosis
- Gynaecological operations
- Operating on the chest or thorax
- General surgery
- Colorectal Surgery
- Treatment involving the head and neck
Advantages of Robotic Surgery
Among its many benefits is the potential for less invasive surgical procedures. In addition to these advantages of robotic surgery, it offers the following:
- The robotic arm’s actions are more precise than a human hand’s. They may also move farther than before. When working in confined areas, the arms allow for rotations of devices that would be impossible for a human.
- An advanced camera delivers enlarged, high-definition images of the surgery region, allowing for better visibility. It also offers better 3D imaging capabilities than the human eye.
- Small devices allow doctors to do specific surgical procedures within your body when previously they would have needed to create a broader incision to access the area from the outside.
Robotics in Surgery: What to Expect
In robotics and computers in surgery, the surgeon doesn’t have to be over the patient physically as in a typical operation. From a nearby console, they may direct the operation and ensure its success. While every case is different, the processes typically taken during a robotic treatment are outlined below.
- A cut no longer than one or two centimetres is made on the patient’s skin.
- The surgeon inserts a micro robotic device and a camera through the incision to reach the surgical site.
- After gaining a clear and enlarged picture of the surgical site, the surgeon controls the surgery via a console or computer.
- The instruments within the body respond precisely to the inputs made at the console in real time.
- Since the robotic devices are more flexible and precise, the surgeon may undertake delicate procedures in previously inaccessible areas.
Conclusion
You can get high-quality care with much-reduced recovery time using robotics in surgery. A highly skilled surgeon makes just tiny incisions and operates with the aid of robotic equipment. Conditions affecting the heart, digestive tract, bladder, prostate, and other organs may all be addressed using robotic surgery.
Less blood loss, shorter hospital stays, and faster recovery times are all advantages of robotic surgery. The best results are often achieved by surgeons who have conducted several such surgeries. Discuss the benefits and risks of robotic-assisted surgery with your doctor.